Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Resistance, Ohm's Law, Ohm's Law in Vector Form, Resistance of a Wire, and Microscopic View of Electric Current.
Important Questions on Ohm's Law
A wire of resistance is gradually stretched to double its original length. It is then cut into two equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel across a battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
A voltage of is applied across a carbon resistor with first, second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours respectively. Calculate the value of current, in , through the resistor.
In the electrical network shown in the figure, the potential difference across resistance will be
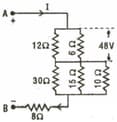
Two identical cells whether connected in parallel or in series gives the same current when connected to an external resistance Find the value of internal resistance of each cell.
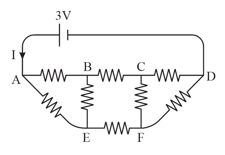
The figure given below shows a network of eight resistors, each equal to connected to a battery of negligible internal resistance. The current in the circuit is
A thick wire is stretched, so that its length becomes two times. Assuming that there is no change in its density, then what is the ratio of change in resistance of wire to initial resistance of wire ?
What is the SI unit of electrical resistance?
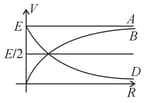
A cell of emf having an internal resistance is connected to an external resistance . The potential difference across the resistance varies with as shown by the curve,
In the figure the potential difference across resistor is . Then the potential difference between and is
A graph drawn between current and voltage in a conductor is as shown in the figure. The changes in the resistance in and parts respectively
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by . Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be
The specific resistance of a wire is its volume is and its resistance is ohms, then its length will be:-
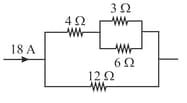
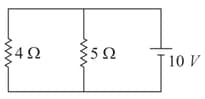
In the following diagram current in the resistor is (when the internal resistance of the battery is zero) :-
A wire of resistance is used to wind a coil of radius . The wire has a diameter of and the specific resistance of its material is . The number of turns in the coil is
Find the radius of the wire of length needed to prepare a coil of resistance ( Resistivity of material of wire is )
A potential of is applied across the ends of a cylindrical copper rod of length and radius . Find the value of the current through the rod. (The resistivity of copper is .)
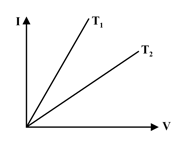
The voltage current graph of conductor at two different temperature are shown in the Figure. If the resistances corresponding to these temperatures are and then which of the following statements is true.
A battery is connected to the terminals of a long wire of uniform thickness and resistance of The difference of potential between two points on the wire separated by a distance of will be
Electrical resistivity of a given metallic wire depends upon
The masses of the three wires of copper are in the ratio of and their length are in the ratio of . The ratio of their electrical resistance is,
